11/21-22/2016
Topic: Periodic Table
Objectives:
- Describe that as you move from left to right in a period (row) on the Periodic Table, the number of protons increases by one.
- Describe that elements found in the same group/family (column) have the same properties.
- Recognize that elements are grouped in the Period Table of Elements according to their properties.
Periodic Table Vocabulary:
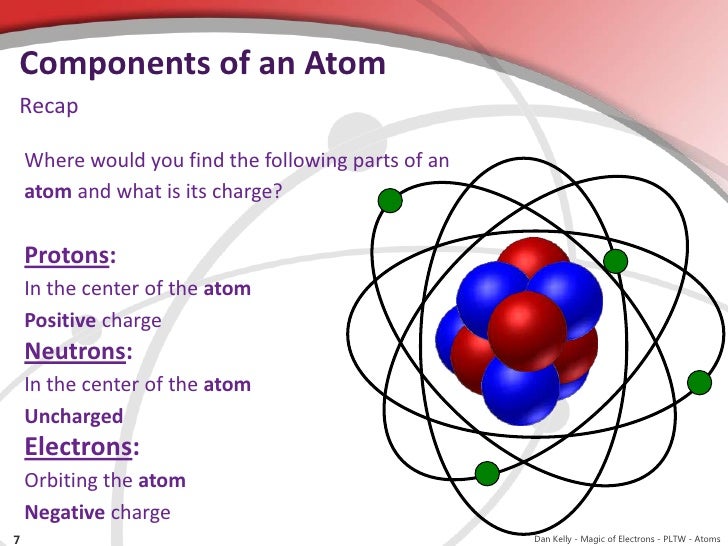
- Atom
- Element
- Proton
- Neutron
- Electron
- Atomic Number
- Periodic Table
- Group or Family (Column)
- Period (Row)
Reference Pages:
- ScienceSaurus: Periodic Table page 265
- Fusion Science Textbook pages 377-387
Periodic Table Literature Connection
Periodic Table Notes
Students will copy Periodic Table reference notes in their Interactive Journal.
- Atomic Number is defined as the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.Every atom of the same element has the same number of protons.
- The number of protons determines the identity of the element.
- Typically atoms have the same number of protons, neutrons and electrons.
- The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
- The periodic table is arranged in horizontal rows of increasing atomic number from left to right. It is also organized into vertical columns with similar characteristics.
- Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons and electrons. These particles can be distinguished based on mass, location and charge.
- Protons: 1 amu (atomic mass unit), in nucleus, positively charged
- Neutrons: approximately 1 amu, in nucleus, neutral charge
- Electrons: negligible mass, outside nucleus, negatively charged.
- Period Number = Number of Energy Levels
- Valence electrons increase moving left to right across the period.
- Groups = Families. Groups have similar properties!
- Acidity increases from Group 1 to Group 18
- Solubility of Metal salts decreases from Group 1 to Group 16
- Metal Salts in water conduct electricity
- Non-metal molecules do not conduct electricity in water
- Solubility is unrelated to element type
Group 1 elements react explosively with water
Periodic Table Videos
Periodic Table Tutorial(s)