Topic: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Objectives:
- SC.8.L.18.1 Describe and investigate the process of photosynthesis, such as the roles of light, carbon dioxide, water and chlorophyll production of food release of oxygen. (Complexity: High)
- SC.8.L.18.2 Describe and investigate how cellular respiration breaks down food to provide energy and releases carbon dioxide. (Complexity: High)
Home Learning:
- Study for vocabulary test on 12/15/2016 (A DAY) or 12/16/2016 (B DAY)
- Complete any assignments not finished during class.
- Achieve 3000 article Water these plants? Maybe not ( due 12/16/2016).
- Complete PENDA activity Cellular Respiration.
Station 1
- Watch, analyze, and take the quiz from Study jams on Photosynthesis Video (Click the video title). It is not required to send or write the answers down in your Interactive Journal.
Station 2
- Watch and take notes in your Interactive Journal from the Photosynthesis Tutorial (Click the tutorial title).
Station 3
- Complete PENDA activity on Cellular Respiration.
Station 4
- Complete Achieve 3000 article Water these plants? Maybe not.
Reference Images
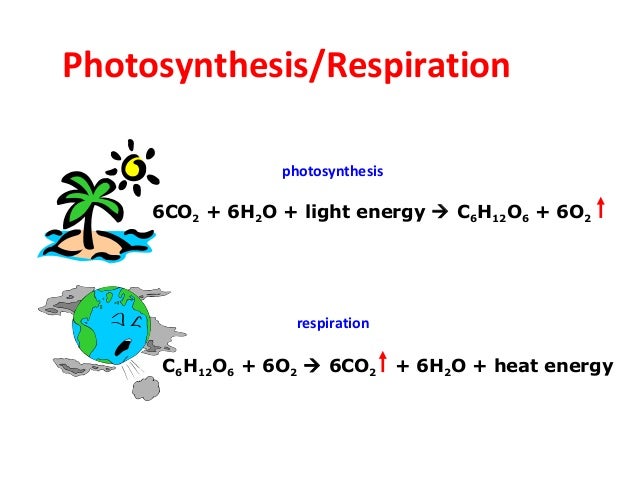

**** NOTE****
It is required to know the formula (Word and Chemical) in order to master the standard.